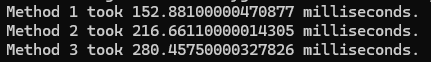Why
This code sample and measuring of speed happened after one code review I was given and I wanted to share it since I got really surprised by coercion speed in JS and how some obvious choices happen to be slower than expected.
The problem
My problem was to take string with date and time in en-US format and check if this string is parsable to date object in JS.
Code I wrote first
isNaN(new Date('2022-01-01'));was my obvious choice once I investigated some articles about how to check if string is valid Date.
However the code was written in TypeScript and only type that is expected in
isNaN(number);is number so I was searching for a way how to (maybe) make one small step and please TypeScript and have everything IMO still readable.
I was reading through what happens when I call
isNaN(Date());and everywhere I looked this should happen “automagically”
isNaN(new Date('2022-01-01').valueOf());so why not call it directly then. TypeScript is happy, it doesn’t hurt readability (that much), but let’s wait what tests will say.
Making it faster
Then I discussed with other colleagues and somehow (shame on me) I forgot about this guy
isNaN(Date.parse('2022-01-01'));OK so now we have 3 ways of checking, all work, but which one is faster? I suppose no one expected the results but here they are.
Measurements
Link to test in your browser https://jsperf.app/mococo.
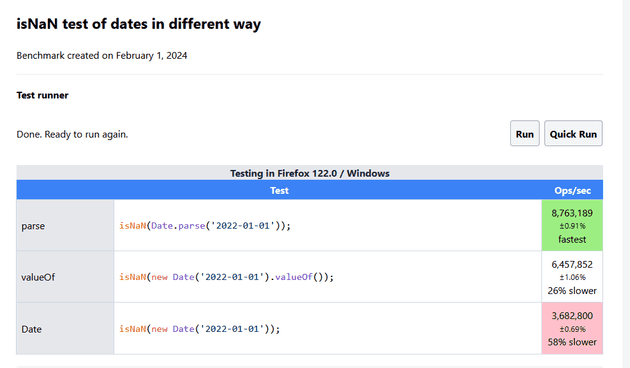
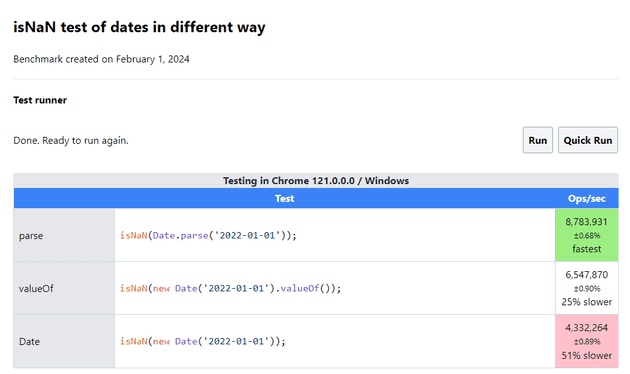
My results in latest browsers :
I surely would expect Date.parse to be fastest but I would really not guesses that there is some difference calling isNaN with just Date vs Date.valueOf(). Maybe someone can explain (drop me an email pls).
NodeJS results
Small snippet for NodeJS here :
const iterations = 1000000;
const date = '2022-01-01';
// Method 1: isNaN(Date.parse(date))
let start = performance.now();
for (let i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
isNaN(Date.parse(date));
}
let end = performance.now();
console.log(`Method 1 took ${end - start} milliseconds.`);
// Method 2: isNaN(new Date(date).valueOf())
start = performance.now();
for (let i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
isNaN(new Date(date).valueOf());
}
end = performance.now();
console.log(`Method 2 took ${end - start} milliseconds.`);
// Method 3: isNaN(new Date(date))
start = performance.now();
for (let i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
isNaN(new Date(date));
}
end = performance.now();
console.log(`Method 3 took ${end - start} milliseconds.`);with NodeJS 20.10.0 I see results like this :
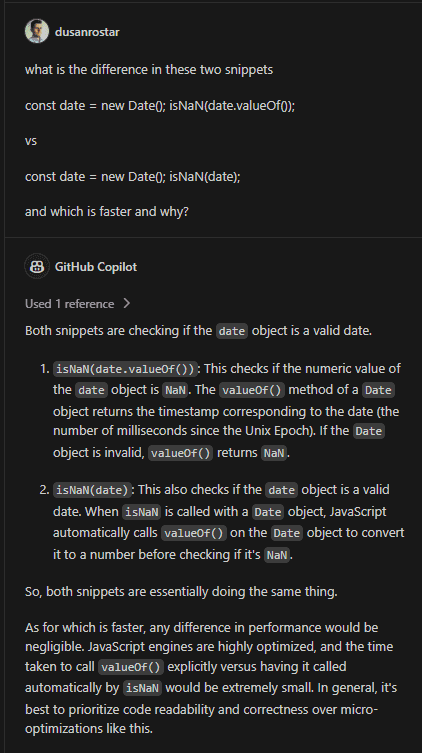
And the bonus from Copilot
Hope this helps.